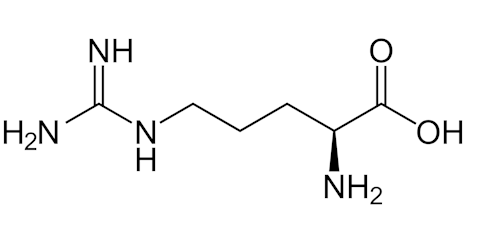
Study
The Australians gave half of the subjects a supplement that provided 9 grams of arginine daily. The other half received a supplement with only 4.5 grams of arginine. In all respects, the subjects were similar.
The researchers used a supplement marketed as Arginaid, a product of Nestle Health Science. Nestle did not sponsor the study.
Arginaid is a powdered supplement packaged in sachets. Users tear open the sachets, dissolve the powder in a glass of water, and then drink it.
Each sachet contains 4.5 grams of arginine, 4 grams of carbohydrates, 155 milligrams of vitamin C, and 40 milligrams of vitamin E. Subjects in one group used one sachet per day, while the other group used two sachets.
Results
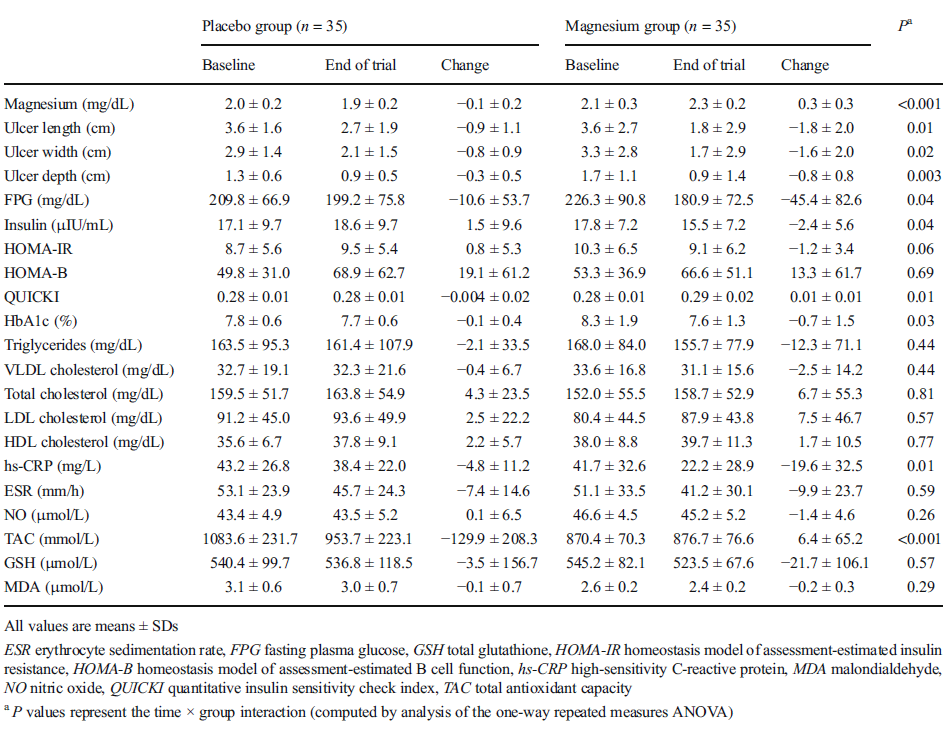
The researchers followed the subjects for three weeks. During this period, the wounds in both groups healed almost equally well.
Based on the measured progression, the researchers estimated that the wounds of the average subject in the 4.5 gram group could heal in 8.7 weeks. In the other group, this would happen in 8.3 weeks. This difference was not statistically significant.
Diet was a factor in both groups. The wounds of malnourished subjects healed more slowly than those of subjects with poor nutrition. This is shown in the figure above.