|
Definition: "An ergogenic aid is any substance or phenomenon that enhances performance "
|
|
||||||||
07.06.2016 |
|
|
Low-inflammatory-index diet protects against cancer
French researchers are studying a diet that reduces the chance of developing cancer and may also extend life expectancy. The diet reduces the synthesis of inflammatory factors such as interleukin-1-beta and tumour necrosis factor alpha. The features of the diet? Large amounts of vitamins, tea, turmeric, good fatty acids, magnesium and selenium, herbs, peppers, fibre and garlic. And according to a study published in the Journal of Nutrition, this type of diet doesn't work if you drink too much alcohol.
Diet Inflammatory Index
So a diet that reduces the synthesis of inflammatory factors should in theory reduce the chance of cancer developing. And because aging is accompanied by a cascade of inflammatory reactions, a diet like this may also increase life expectancy. That's our surmise, which we simple compilers of this webzine pass on to you freely.
The more calories you consume daily, and the more carbohydrates, bad fats, proteins, cholesterol, vitamin B12 and iron you consume, the more inflammatory factors your body produces. Nutritional factors that reduce the synthesis of inflammatory factors include unsaturated fatty acids, fibre, magnesium, beta-carotene, vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B6, B11, C, D, E, anthocyanidins, flavan-3-ols, flavonols, flavanones, flavones, isoflavones, garlic, ginger, pepper, onions, tea, eugenol, saffron, selenium, turmeric, zinc, thyme, oregano and rosemary.
Study
Results
But when the researchers analysed their data, they discovered that alcohol also played a role in the protective effect of a low-inflammatory-index diet. That's not so surprising: alcohol exacerbates inflammatory processes. The positive effect of a diet with a low inflammatory index is negated when high levels of alcohol are consumed.
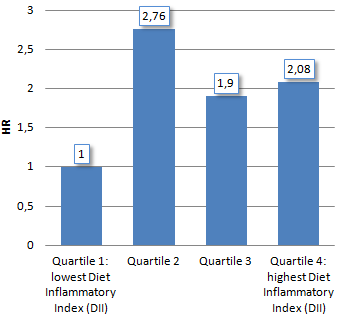
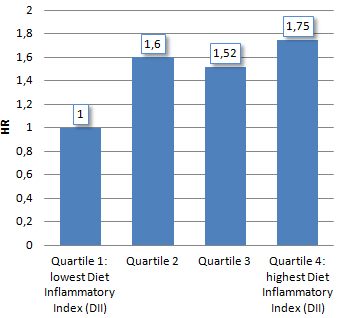
And hey presto: [Table] the table below shows that a diet with a low inflammatory index offered better protection against cancer in the group that consumed low amounts of alcohol. Low alcohol consumption means a daily maximum of 0.6 glass for women and a maximum of 2.4 glasses a day for men.
Among the women who drank little alcohol, a diet with a low inflammatory index reduced the chance of developing breast cancer by a factor of four.
Conclusion
"Consistent with mechanistic data, our results suggest that a proinflammatory diet may be associated with increased prostate cancer risk. When models were stratified by alcohol intake, a major cancer risk factor, a pro-inflammatory diet also was associated with increased overall and breast cancer risk in low-to-moderate drinkers."
"These results provide interesting insights for the understanding of the relations between diet and cancer risk, and inflammation-based underlying mechanisms. They suggest that promoting an anti-inflammatory dietary pattern may contribute to cancer prevention."
Source:
More:
Archives: |
|