|
Definition: "An ergogenic aid is any substance or phenomenon that enhances performance "
|
|
||||||||
24.02.2021 |
|
|
Fighting obesity with semaglutide | Just as effective as bariatric surgery?
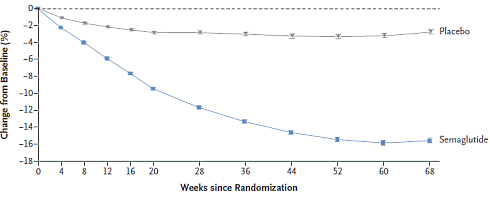
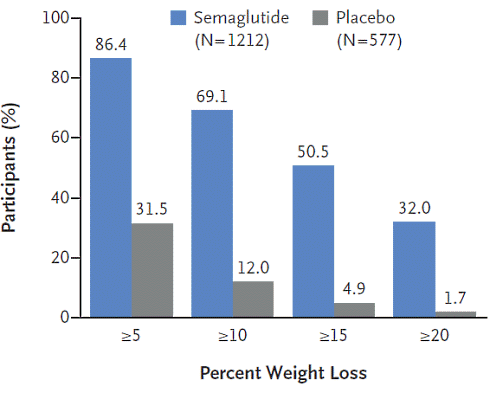
"For the first time, people can achieve through drugs what was only possible through weight-loss surgery", British professor and endocrinologist Rachel Batterham says in a press release. [sciencedaily.com, February 11, 2021.] The drug Batterham is talking about is semaglutide. In a trial soon to be published in the New England Journal of Medicine, obese subjects lose an average of 15 pounds when they use semaglutide.
Semaglutide
GLP-1 administered exogenously is rapidly cleared from the body, but semaglutide is altered in such a way that it continues to circulate for an extended period of time. The enzymes that split GLP-1 into pieces quickly have difficulty with semaglutide.
In the NEJM trial, the obese subjects only had to inject themselves with a semaglutide pen once a week.
Study
The starting dose was 0.25 milligrams of semaglutide per injection, but the dose gradually increased to 2.4 milligrams over the first 16 weeks of the trial. Some subjects were unable to tolerate this 2.4 milligram dose and kept using a lower amount.
The researchers used a Novo-Nordisk product. Novo-Nordisk produces injectable semaglutide, but also semaglutide in tablet form. Diabetologists and endocrinologists already give it at a lower dose to people with diabetes. Novo-Nordisk sponsored the trial.
Results
The subjects in the experimental group lost a significant portion of their waist size. In addition, their cholesterol balance improved. Finally, the subjects also reported an increase in their quality of life.
Side effects
According to the study in the NEJM, semaglutide is relatively safe. You should also bear in mind that semaglutide is a new drug, the side effects of which have not yet been identified. We know of other older GLP-1 agonists, that they may have side effects that users should take seriously.
There arte some indications that the older GLP-1 analogues may damage the kidneys in some users. [Gebu 2009;43:103-4.] In addition, the US FDA is aware of some instances where users of GLP-1 analogues have developed inflammation of the pancreas. Some of these cases were fatal. [Gebu 2010;44(5):49-55.]
Source: More: Archives:
|
|
|||||||||||||||