|
Definition: "An ergogenic aid is any substance or phenomenon that enhances performance "
|
|
||||||||
23.06.2017 |
|
|
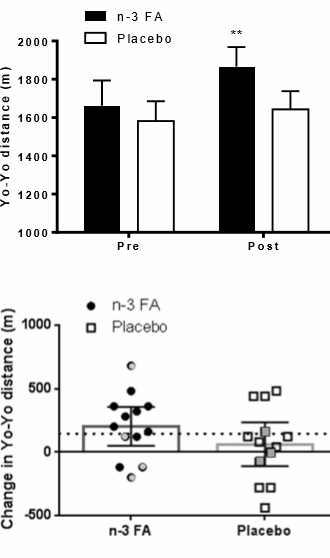
EPA-rich fish oil boosts footballers' endurance capacity
Study
A control group of 13 different footballers took a placebo.
Results
The supplementation did results in considerably better scores in the Yo-Yo level 1 test.
The Yo-Yo test gives a good indication of the endurance capacity that footballers will have during matches. [Sports Med. 2008;38(1):37-51.]
The test involves sprinting a distance of 20 metres in increasingly shorter times, and walking a distance of 10 metres during a10-second period between sprints. The test continues until you can no longer sprint the 20 metres in the allotted time. The score is the total amount of metres covered.
Conclusion
"We also can conclude that 4 weeks of n-3 fatty acids supplementation did not improve strength, power or speed assessments of physical function, nor tests of respiratory function."
"The dose of n-3 fatty acids administered in this study was a high dose provided on a body mass adjusted basis to maximise incorporation of n-3 fatty acids into cell membranes, and this ingestion is unlikely to be feasible for all soccer players."
"Future studies should investigate the dose response effect of n-3 fatty acids supplementation on training induced outcomes, or examine whether a loading dose followed by a maintenance dose can sustain the lipid changes observed."
Source:
More:
|
|
||||||||||||||||