|
Definition: "An ergogenic aid is any substance or phenomenon that enhances performance "
|
|
||||||||
08.12.2016 |
|
|
The unsuspected anabolic effect of AKG (in massively high doses)
Study
Results
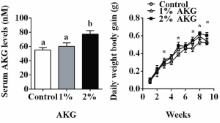
AKG had no effect on the weight of the liver. So it doesn't look like AKG in these doses causes liver damage. At the same time, the supplementation resulted in an increase in muscle mass and a reduction in fat mass.
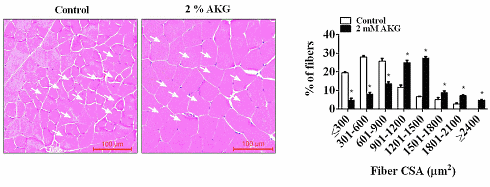
The figures above show that the increase in muscle mass was a consequence of hypertrophy. AKG resulted in a big increase in the dimensions of the muscle fibres. The figure below shows that AKG activates the classic anabolic signal molecules like mTOR and Akt in the muscle cells.
So AKG works through this receptor. The receptor family that GPR91 belongs to 'sees' metabolites that are released during the citric acid cycle - like AKG. The GPR99 receptor, which bears a striking resemblance to GPR91, 'sees'... AKG. [Nature. 2004 May 13;429(6988):188-93.] So GPR91 would seem to do the same.
Conclusion
Two slight grumbles in our concluding remarks. Uno: muscle cells of mice contain many GPR91-receptors, but whether that's also the case for human muscle cells? We have no idea. Duo: In the doses we're talking about here, AKG probably raises blood pressure, and has other side effects too. So make sure you read up properly before starting to experiment with high doses of AKG. A suggestion: [Cell Commun Signal. 2016 Jan 12;14:3.]
Source:
More:
Archives: |
|