|
Definition: "An ergogenic aid is any substance or phenomenon that enhances performance "
|
|
||||||||
01.07.2011 |
|
|
Steroids speed up Alzheimer's, in cell study
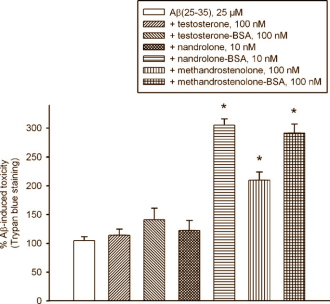
Long-term use of high doses of anabolic steroids makes brain cells more sensitive to the beta-amyloid peptides that cause damage and kill brain cells in Alzheimer's disease. Pharmacologists from the University of Catania draw this conclusion from experiments they did, in which they exposed rats' brain cells to testosterone, nandrolone and methandrostenolone [the active ingredient in Dianabol].
The letters BSA at the end of a word indicate that the substance is an oxime derivate. The researchers reasoned that, in cell studies, oximes would only be able to react with receptors on membranes.
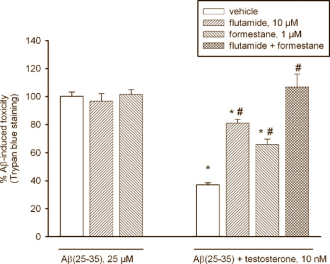
They conducted experiments using cells from the cortex of embryonic rats. They left them for 48 hours in test tubes, and when they added steroids the cortex cells died. When they added flutamide, and anti-androgenic, the toxic effect disappeared.
Methandrostenolone doesn't do much with the androgen receptor, but it's not a progestagen either. The researchers have no idea why RU486 has this effect. All they say is that we don't yet understand how methandrostenolone works.
When the researchers added the toxic beta-amyloid peptides [A-beta] to the cells, the first thing they noticed was that testosterone in a low concentration protected the brain cells, but that this protective effect disappeared when the anti-androgen flutamide and the anti-oestrogen 4-hydroxy-androstenedione were added. On the other hand, they also noticed that higher androgen doses increased the rate of death of the brain cells by the beta-amyloid peptides.
The researchers wonder whether what they observed in their test tubes also takes place in the brains of steroids users. If this is the case, then the list of potential side effects of steroids use has just become a little longer. "Exposure to anabolic androgenic steroids may result in a compromised brain, more susceptible, later in life, to the onset or progression of diseases not usually linked to drug abuse, especially neurodegenerative diseases", the researchers conclude in their article.
Source:
More:
|
|