|
Definition: "An ergogenic aid is any substance or phenomenon that enhances performance "
|
|
||||||||
06.11.2015 |
|
|
Physical exercise boosts concentration of longevity hormone
We recently wrote about the longevity hormone klotho: it delays aging, reduces age-related symptoms and helps us to stay fit and healthy in old age. Physical exercise can help increase the amount of this hormone that the body produces, researchers at the University of Pittsburgh report in Frontiers in Physiology. If your condition isn't too bad to start with, at least.
Forms of klotho
What beta-klotho does exactly is not yet known.
Alpha-klotho functions as a rejuvenating hormone. You can read more about this here. So whenever scientists mention klotho, they are nearly always referring to alpha-klotho. The figure below, from a publication in Nature by the Japanese scientists who discovered klotho, shows the tissues that synthesise alpha-klotho. [Nature. 1997 Nov 6;390(6655):45-51.]
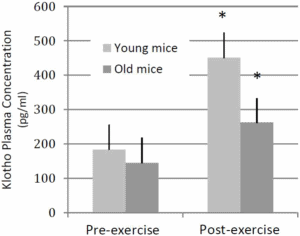
Muscles produce klotho, and exercise speeds up the metabolic rate of muscle cells. So are active muscles capable of producing more klotho if they get more exercise? That's the question that the researchers set out to answer by doing animal and human studies.
Animal study
Human study
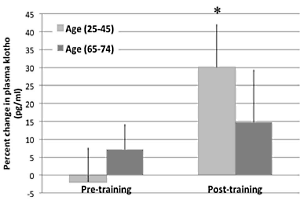
In the figure below the bars on the left show that this exercise did not lead to a significant rise in concentration of klotho in the blood.
The researchers then got their subjects to train on treadmills, cycles and rowing machines 4-6 times a week for 12-16 weeks. At the end of this period the researchers repeated the hour-long trial. And this time the exertion did lead to a rise in the klotho level, as you can see in the figure above on the right.
Conclusion
"While this response to an acute exercise bout and training appears, from the current results, to be attenuated in older individuals, it should be noted that the training protocol for the aged individuals was slightly less intense and of a shorter duration than that of the young individuals." "These differences in training intensity may confound the age-related differences in the response of klotho to acute exercise and further clinical studies are warranted. However, in our murine studies, where the exercise intensity was matched across age groups, a similar age-related decline in the klotho response following an acute exercise bout was also observed." "Modulation of klotho expression through skeletal muscle contraction represents an intriguing relationship that may help explain the anti-aging effects of physical activity, and, as highlighted in this review, there is emerging evidence to suggest that such a relationship exists."
Source:
More:
Archives:
|
|