|
Definition: "An ergogenic aid is any substance or phenomenon that enhances performance "
|
|
||||||||
15.03.2017 |
|
|
Beetroot better for athletes than sodium nitrate
Athletes react better to beetroots - in the form of vegetables from the supermarket or juice concentrate - than to sodium nitrate. Researchers at the Swiss Institute of Sports Medicine discovered this. Yes, nitrate is the most important active ingredient in beetroot, but apparently beetroot also contains other substances that boost the performance enhancing effect of nitrate.
Study
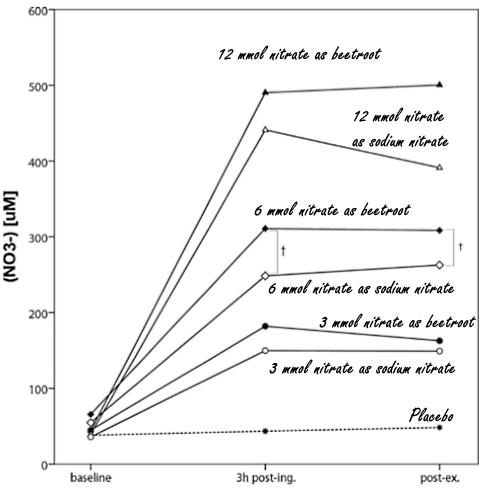
#1 a placebo #2 3 millimoles nitrate in de form of beetroot #3 3 millimoles nitrate in the form of sodium nitrate #4 6 millimoles nitrate in the form of beetroot #5 6 millimoles nitrate in the form of sodium nitrate #6 12 millimoles nitrate in the form of beetroot #7 12 millimoles nitrate in the form of sodium nitrate
Three hours after intake the men had to cycle at high intensity for eight minutes.
Results
3 h post-ing. = three hours after ingestion; post-ex. = after exercise.
There was a subtle difference between the effect of beetroot on the subjects' blood pressure and that of sodium nitrate. Beetroot reduced blood pressure slightly more than sodium nitrate did.
Both beetroot and sodium nitrate reduced oxygen consumption during the intensive exercise. [That's why beetroot is so interesting for athletes: it helps the body use oxygen more efficiently.] And, yes you've guessed it - beetroot reduced the body's oxygen needs more than sodium nitrate did.
Conclusion
"Overall, beetroot juice seems to be more effective in terms of lowering VO2 [...] compared with nitrate. These differences may originate from the facilitated nitrite conversion to NO, which may have been catalyzed by polyphenols, vitamin C, and other antioxidants present in the beetroot juice, in combination with nitrate."
Source:
More:
Archives: |
|