|
Definition: "An ergogenic aid is any substance or phenomenon that enhances performance "
|
|
||||||||
28.07.2011 |
|
|
Strength training + soya protein shake help women slim faster
Strength training is a great way to achieve a healthy weight, if you're prepared to take a long-term approach. Each pound of muscle mass gained leads to a rise in the amount of calories your body burns each day. You can strengthen that effect by including 25 g extra soya protein in your diet, Brazilian researchers discovered.
Study
The protein shake contained 25 g soya protein and 50 mg isoflavones: 32 mg genistein, 15 mg daidzein and 3 mg glycitein.
Results
The protein shake did not boost the increase in muscle mass, but it did boost energy expenditure while resting [REE].
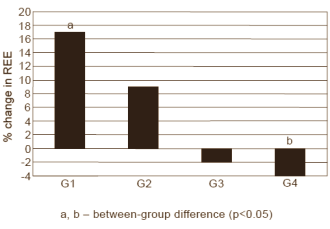
The researchers measured the subjects' REE before and after the 160 weeks. At the time that measurements were taken, the women hadn't eaten for at least 12 hours and hadn't trained for 24 hours. The figure below shows that the G1 group used up 17 percent more calories when resting than the G0 group did. That's the equivalent of 158 calories daily. In the G2 group the increase was 9 percent – which amounts to 110 calories more per day.
So doing a quick calculation: in the G1 group, one kilogram extra of muscle mass increased the daily calorie burning at rest by 119 calories. In the G2 group, one kilogram extra of muscle mass increased the daily calorie burning at rest by 54 calories. This is a calculation that would make scientists shudder, but it gives an idea.
Conclusion
The study did not examine any other types of protein. The researchers believe however that the energy expenditure boost is caused by the isoflavones. These stimulate the energy production, according to the researchers.
The research was funded by the state of Sao Paulo. The soya industry is one of the most important sectors of the economy in Sao Paulo.
Source:
More:
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||