|
Definition: "An ergogenic aid is any substance or phenomenon that enhances performance "
|
|
||||||||
30.12.2022 |
|
|
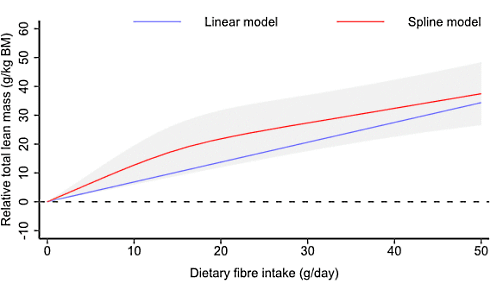
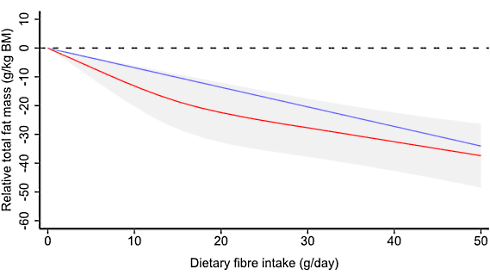
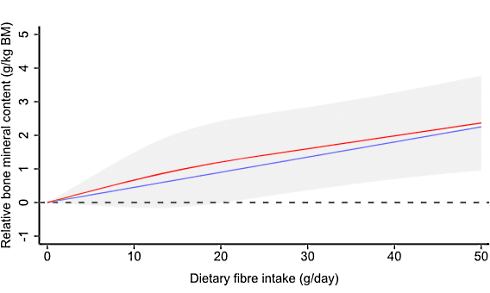
More dietary fiber, more muscle (and less body fat)
The more dietary fiber you eat on a daily basis, the more muscle mass you probably have and the lower your fat mass is. Is this because dietary fiber increases your sensitivity to insulin? Or is there more going on?
Study
One dataset related to fiber intake and body composition, another to fiber intake and insulin metabolism, and yet another to fiber intake and hand grip strength. In fact, we are talking about three different studies.
Results
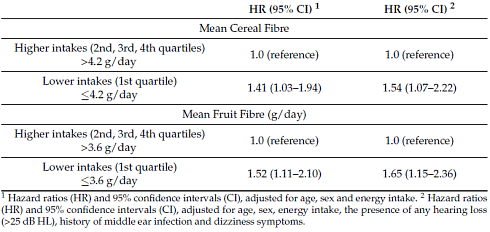
In addition, the study participants with a lot of fiber in their diet were stronger. This is clear from the table below.
The associations persisted after the researchers had brushed away the effect of, among other things, the total energy intake. It was therefore not the case that people who consumed a lot of fiber also ate more, apparently exercised more and therefore had stronger muscles.
Mechanism
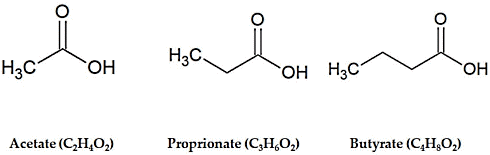
According to epidemiological research, people over fifty have more muscle strength the more dietary fiber they consume. That may be because the short chain fatty acids, which are created when probiotica ferment fibers, stimulate the biosynthesis of mitochondria in older muscle cells.
We have written before about the associations between dietary fiber, pre- and probiotics and anabolism. Links to these posts can be found at the bottom of this page.
Conclusion
"Moreover, the improvements in body composition with higher dietary fibre intakes are allied with improvements in glucose homeostasis and skeletal muscle strength."
"Future research should look to evaluate the therapeutic potential of increasing dietary fibre intake (via diet modification and/or supplementation) on skeletal muscle and associated outcomes, with a focus on the preservation of skeletal muscle mass in adults aged 40 years and older."
Source: More: Archives:
|
|
|||||||||||||||||