|
Definition: "An ergogenic aid is any substance or phenomenon that enhances performance "
|
|
||||||||
02.08.2023 |
|
|
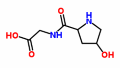
Glyoxylic acid, a glycine metabolite with an anabolic effect
Glyoxylic acid is a metabolite of glycine. Glyoxic acid is created when the body converts glycine into energy. According to a Japanese in vitro study, glyoxylic acid has an anabolic and an anti-catabolic effect.
Glyoxylic acid
Doctors use alpha-keto acids if they want to slow down muscle breakdown in people with a metabolism that can process little urea and ammonia. Manufacturers of sports nutrition use alpha-keto acids to make amino acids such as arginine and ornithine more effective.
There are indications that alpha-keto acids are interesting sources of energy for athletes and, in large doses, inhibit muscle breakdown. Recent animal studies and human studies also suggest that the alpha-keto acid alpha-ketoglutarate AKG slows down aging processes. The related alpha-ketobutyrate also does this in fundamental research.
Study
Results
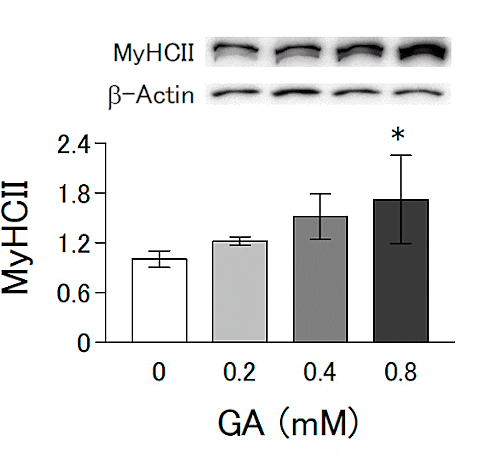
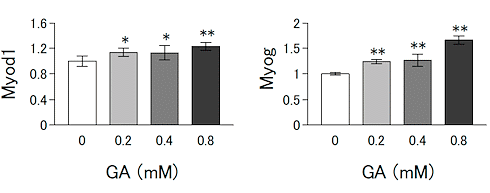
At the same time, glyoxylic acid increased the activity of the genes Myod1 and Myog in the muscle cells. The activity of those genes distinguishes mature and functional muscle cells from immature muscle cells.
Exposure to glyoxylic acid increased the amount of mitochondrial DNA [mtDNA]. The glycine metabolite apparently stimulated mitochondrial biosynthesis in muscle cells. This allows muscle cells to generate more energy.


Mechanism
Conclusion
The researchers are aware that, according to textbooks, glyoxylic acid may contribute to the formation of kidney stones. Glyoxylic acid is a precursor of oxalic acid, so that idea is not so strange. But whether glyoxylic acid causes kidney stones to form in real life has never been properly investigated.
"Currently, glyoxylic acid may be regarded as a substance that induces ureteral stones", the Japanese continue. "However, in the future, it may be an important nutrient for promoting myogenesis in skeletal muscle, similar to keto acid analogs derived from essential amino acids without producing urinary toxins."
Source: More: Archives:
|
|
|||||||||||||||||