funder of both studies.
There are 2 major differences between the studies. The subjects in yesterday's study were healthy but untrained men, the subjects in this study were trained women, who had been training for at least three years. That's 1.
In addition, the women in this study took not 300 but 600 milligrams of CurraNZ per day. That's 2.
In an earlier study, the researchers had discovered that trained endurance athletes do not respond to a dose of 300 milligrams, but they do respond to higher doses. [Eur J Appl Physiol. 2017 Jun;117(6):1207-16.] The women divided their doses over two intake times per day. They took a capsule of 300 milligrams for breakfast, and then another capsule 12 hours later.
After a period of 7 days in which the subjects had taken a placebo or a supplement daily, the researchers got the women to cycle for 2 hours at an intensity of 65 percent of their maximum oxygen uptake.
Results
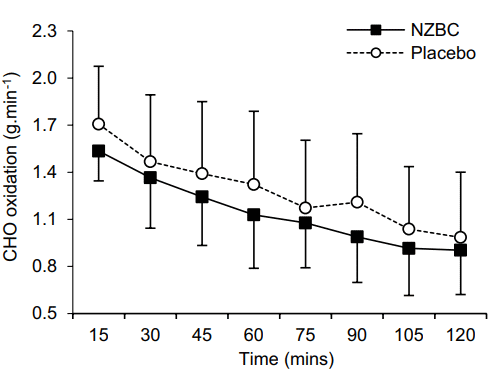
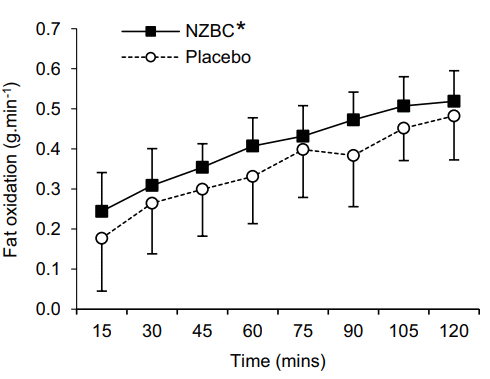
The British found no effects of CurraNZ on the maximum oxygen uptake, heart rate or total energy expenditure of the women. They did find that after seven days of supplementation, the women burned 27 percent more fat during their sessions.
The researchers found a tendency for the women to consume fewer carbohydrates during their session after supplementation. However, the difference with the burning of carbohydrates after administration of a placebo was just not statistically significant.

Mechanism
Based on the scientific literature, the British suspect that active substances in blackcurrant make fat cells produce more proteins such as hormone-sensitive lipase and perilipin-1. Those proteins make fat cells release more of their contents into the bloodstream. They stimulate lipolysis.
Another possibility, which the above does not exclude, is that the components of blackcurrant directly activate the key molecule AMPK.
Source:
Eur J Appl Physiol. 2018 Jun;118(6):1265-72.