|
Definition: "An ergogenic aid is any substance or phenomenon that enhances performance "
|
|
||||||||
04.06.2016 |
|
|
Elderberries help against colds
A supplement containing an extract of elderberries – scientific name Sambucus nigra – helps the immune system to fight the common cold. Australian researchers at Griffith University published an article on this in Nutrients. If you still develop a cold after taking Sambucus nigra, you'll recover two days faster and your symptoms will be less severe than if you didn't take it.
Sambucus nigra
Before the advent of antibiotics, healers used elderberry juice against infectious diseases. And recent studies show that this wasn't such a bad idea. Animal studies have shown that supplementation with Sambucus nigra extracts protects mice against viruses, [Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2012;76(9):1633-8.] and in test tubes Sambucus nigra extract makes immune cells more aggressive.
Study
The researchers divided their subjects into two approximately equal-sized groups. Ten days before departure the subjects started taking capsules, and continued to do so for the four first days after their arrival. The capsules given to one group contained no active ingredients, but those given to the other group contained an extract of Sambucus nigra. These contained 300 mg extract, consisting of 22 percent quercetin analogues and 15 percent anthocyanins (primarily analogues of cyanidin and perlargonidin). The subjects took two to three capsules a day.
The researchers used extracts made by the Italian company Iprona. [iprona.com] And yes, you can feel what's coming next. Iprona paid for the study.
Results
The subjects who had taken Sambucus nigra and still developed a cold recovered faster than the people in the placebo group who had caught cold. Their symptoms were also less severe than those of the subjects in the placebo group. And yes, these differences were statistically significant.
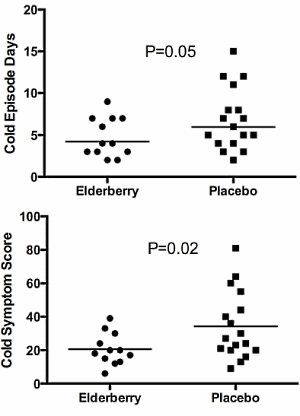
Conclusion
"The incidence of adverse events was low overall and no adverse effects could be directly attributed to elderberry."
"Based on these results it seems worthwhile to undertake more clinical research with high quality elderberry preparations to better understand beneficial health implications of this nutritional traditional medicine."
Source:
More:
Archives: |
|
